9 Differences Between Compression Garments vs. Shapewear


In the world of fashion and healthcare, the terms “compression garments” and “shapewear” (Garments vs. Shapewear: )are often used interchangeably. However, they serve distinct purposes and offer different benefits. This blog post will delve into the key differences between compression garments and shapewear, highlighting their unique features, uses, and benefits. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which option might be best suited for your needs.
1. Defining Compression Garments and Shapewear
1.1. What Are Compression Garments?
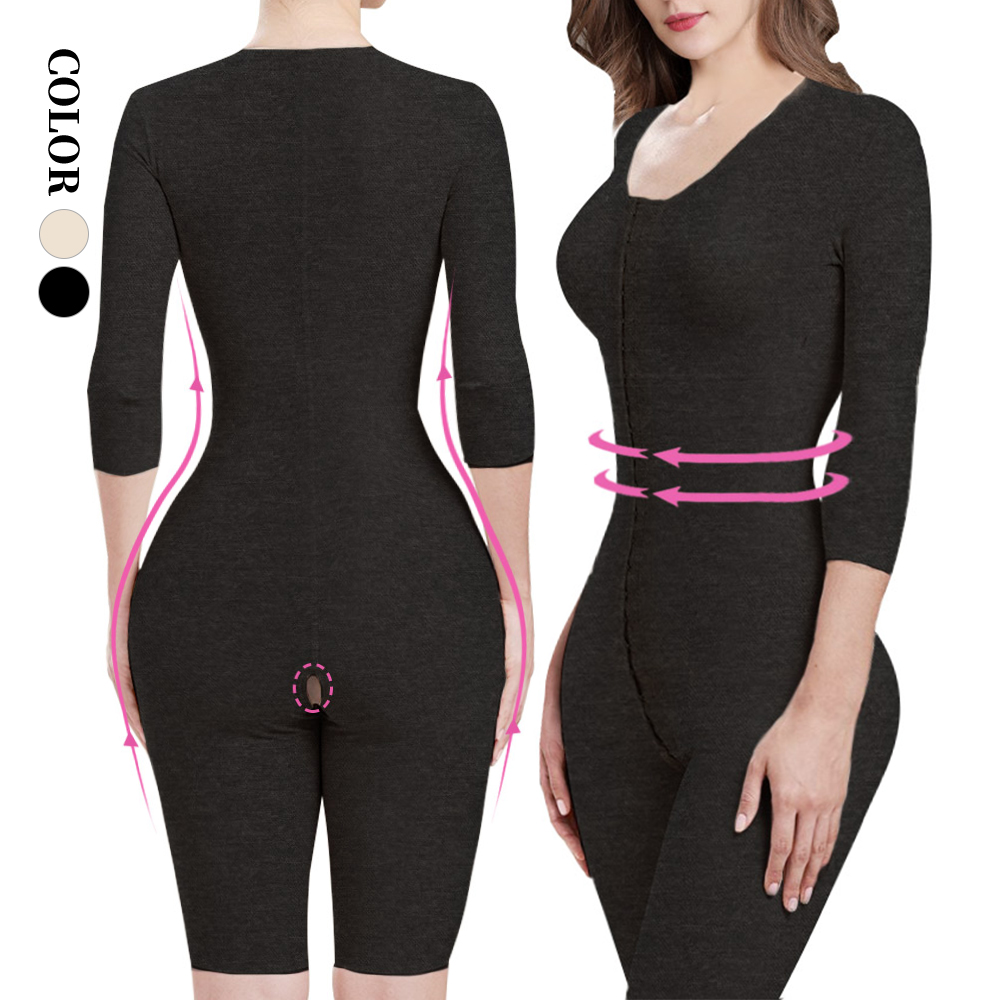
Compression garments are specialized clothing designed to provide graduated pressure to specific areas of the body. They are commonly used in medical and athletic contexts to improve circulation, reduce swelling, and support muscle recovery.
Common Types of Compression Garments:
- Compression socks and stockings
- Compression sleeves
- Compression shorts and tights
- Post-surgical compression garments
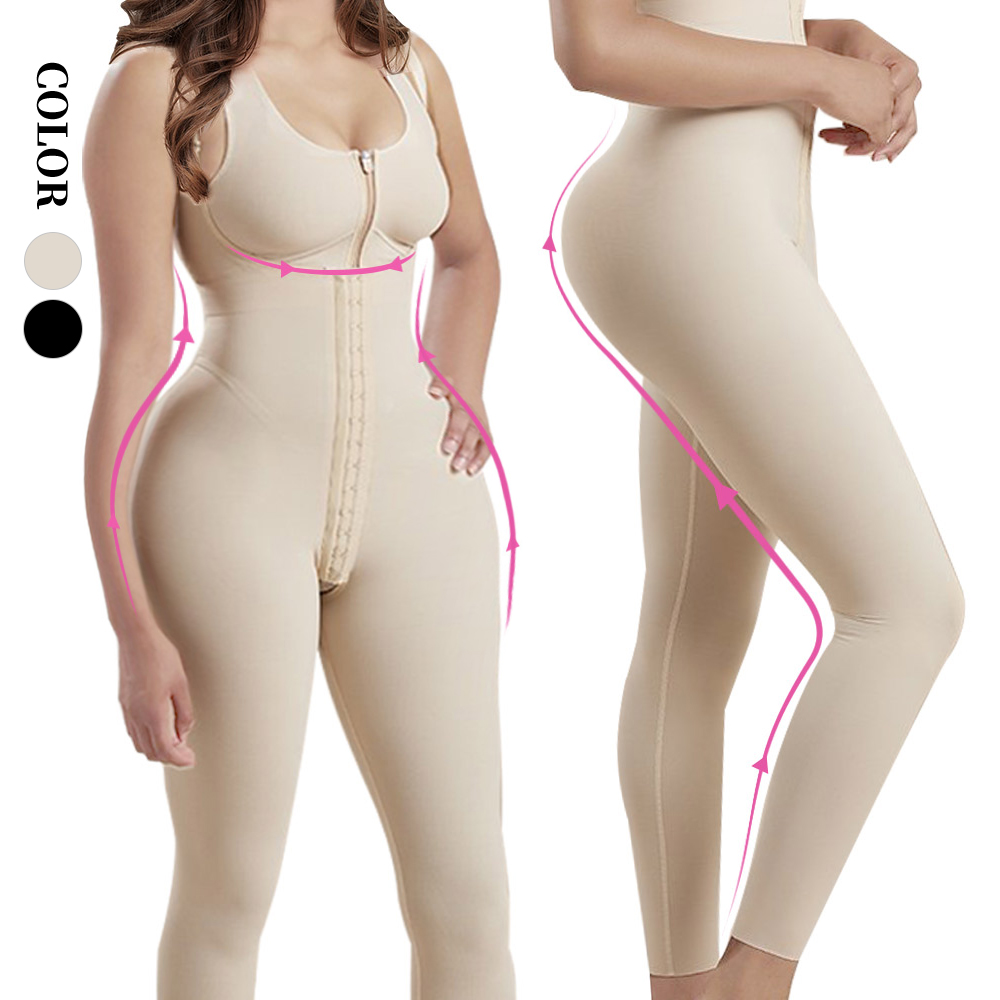
1.2. What Is Shapewear?
Shapewear, on the other hand, is designed primarily for aesthetic purposes. It aims to smooth, shape, and contour the body to enhance the wearer’s appearance. Shapewear can be found in various styles and levels of control, from light smoothing to firm compression.
Common Types of Shapewear:
- Control briefs
- Bodysuits
- Waist cinchers
- Shaping camisoles
- Thigh slimmers
2. Primary Purposes and Benefits
2.1. Purposes of Compression Garments
Medical Use:
- Improving Circulation: Compression garments help increase blood flow, which can be beneficial for individuals with circulatory issues like varicose veins or deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Reducing Swelling: They are often used post-surgery or for individuals with lymphedema to minimize swelling and fluid retention.
- Supporting Muscle Recovery: Athletes use compression garments to reduce muscle soreness and speed up recovery times after intense workouts.
Athletic Use:
- Enhanced Performance: By providing support and reducing muscle vibration, compression garments can enhance athletic performance.
- Injury Prevention: They offer muscle support, which can help prevent injuries during physical activities.
2.2. Purposes of Shapewear
Aesthetic Use:
- Body Contouring: Shapewear smooths and shapes the body, creating a more streamlined silhouette under clothing.
- Boosting Confidence: By enhancing the body’s appearance, shapewear can boost the wearer’s confidence, making them feel more comfortable and stylish in their outfits.
Posture Improvement:
- Supporting Posture: Some shapewear, like waist cinchers, can provide back support and encourage better posture.
3. Material and Design Differences
3.1. Materials Used in Compression Garments
Compression garments are typically made from high-quality, durable materials designed to provide consistent pressure. Common materials include:
- Nylon and Spandex Blends: These materials offer elasticity and durability.
- Moisture-Wicking Fabrics: Many compression garments are designed to wick away sweat, keeping the skin dry and comfortable.
3.2. Materials Used in Shapewear
Shapewear is often made from similar stretchy materials but focuses more on comfort and aesthetics. Common materials include:
- Nylon and Spandex Blends: These provide the necessary stretch and compression.
- Cotton Blends: For added comfort and breathability.
- Seamless Construction: Many shapewear pieces are designed to be seamless, ensuring they remain invisible under clothing.
3.3. Design Elements
Compression Garments:
- Graduated Compression: Provides varying levels of pressure, with the highest compression at the extremities to aid blood flow back to the heart.
- Targeted Support: Specific areas are reinforced to provide support where needed, such as knees or elbows.
Shapewear:
- Paneling and Boning: These elements help contour and shape the body.
- Varied Control Levels: From light to firm control, allowing users to choose the level of shaping they desire.
- Aesthetic Features: Lace trims, seamless edges, and other design features enhance the garment’s appearance and comfort.
4. Usage Scenarios
4.1. When to Use Compression Garments
Medical Scenarios:
- Post-Surgery Recovery: To reduce swelling and support healing.
- Chronic Conditions: For managing symptoms of conditions like lymphedema or varicose veins.
- Travel: To prevent DVT during long flights or periods of inactivity.
Athletic Scenarios:
- Training and Competition: To enhance performance and reduce fatigue.
- Recovery: To speed up muscle recovery after intense exercise.
4.2. When to Use Shapewear
Everyday Use:
- Under Work Attire: To create a smooth silhouette under professional clothing.
- Casual Outfits: For added confidence and a streamlined appearance in everyday wear.
Special Occasions:
- Formal Events: To enhance the fit and appearance of dresses, gowns, and other formalwear.
- Weddings: Brides and bridesmaids often use shapewear for a polished look on the big day.
5. Differences in Fit and Comfort
5.1. Fit of Compression Garments
Compression garments are engineered to provide a snug fit that applies consistent pressure. The fit should be tight but not uncomfortable.
Key Fit Features:
- Graduated Compression: Ensures optimal blood flow and support.
- Snug Fit: Designed to be worn for extended periods without causing discomfort.
5.2. Fit of Shapewear
Shapewear focuses on comfort and aesthetic enhancement. It should fit snugly but comfortably, without causing bulges or restricting movement.
Key Fit Features:
- Seamless Design: To remain invisible under clothing.
- Varied Compression Zones: Different areas may have varying levels of control to shape the body effectively.
5.3. Comfort Considerations
Compression Garments:
- Breathability: Often made with moisture-wicking fabrics to keep the skin dry.
- Extended Wear: Designed for long-term use, such as during travel or athletic activities.
Shapewear:
- Soft Fabrics: Often includes cotton or other soft materials for comfort.
- Daily Wear: Intended to be comfortable enough for daily use but typically not for extended periods.
6. Health Implications
6.1. Health Benefits of Compression Garments
Medical Benefits:
- Improved Circulation: Helps prevent blood clots and reduces symptoms of chronic conditions.
- Reduced Swelling: Effective for managing post-surgical swelling and lymphedema.
- Enhanced Recovery: Speeds up muscle recovery and reduces soreness.
Athletic Benefits:
- Performance Enhancement: Supports muscles and reduces fatigue during exercise.
- Injury Prevention: Provides stability and support to reduce the risk of injuries.
6.2. Health Risks of Compression Garments
- Too Tight: Can cause discomfort or restricted blood flow if not sized correctly.
- Skin Irritation: Prolonged use can lead to skin issues if not properly ventilated.
6.3. Health Benefits of Shapewear
Aesthetic Benefits:
- Enhanced Appearance: Provides a smoother, more contoured look under clothing.
- Boosted Confidence: Can improve self-esteem by enhancing body shape.
Posture Support:
- Improved Posture: Some shapewear offers back support, promoting better posture.
6.4. Health Risks of Shapewear
- Digestive Issues: Tight shapewear can compress the stomach, leading to acid reflux or heartburn.
- Circulatory Problems: Overly tight garments can restrict blood flow and cause numbness or tingling.
- Skin Irritation: Prolonged use can cause rashes or fungal infections, especially in areas prone to sweating.
- Respiratory Issues: Can restrict breathing if too tight around the chest.
7. Cost and Accessibility
7.1. Cost of Compression Garments
Compression garments can be more expensive due to their medical and performance benefits. Prices vary based on the type and quality of the garment.
| Type | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Compression Socks | $20 – $50 |
| Compression Sleeves | $15 – $40 |
| Compression Shorts/Tights | $30 – $100 |
7.2. Cost of Shapewear
Shapewear is typically more affordable, with prices varying based on brand, material, and level of control.
| Type | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Control Briefs | $10 – $30 |
| Bodysuits | $20 – $80 |
| Waist Cinchers | $15 – $60 |
7.3. Accessibility
Compression Garments:
- Availability: Found in medical supply stores, pharmacies, and specialty athletic shops.
- Customization: Some medical compression garments can be custom-fitted.
Shapewear:
- Availability: Widely available in department stores, lingerie shops, and online retailers.
- Variety: A wide range of options in terms of style, size, and control level.
8. Personal Preferences and Lifestyle
Personal Preferences and Lifestyle Considerations
Choosing between compression garments and shapewear often comes down to personal preferences and lifestyle needs. Here’s how to decide which might be best for you:
8.1. Lifestyle Needs
Active Lifestyle:
- Compression Garments: Ideal for athletes or active individuals who need muscle support and recovery aids.
- Shapewear: May not be as suitable for high-intensity activities due to potential comfort issues.
Professional Environment:
- Compression Garments: Beneficial if you have to stand or sit for long periods, as they help with circulation and reduce fatigue.
- Shapewear: Great for looking polished and confident in professional attire.
8.2. Occasional Use vs. Daily Wear
Occasional Use:
- Compression Garments: Typically used during workouts, post-surgery, or during travel.
- Shapewear: Often reserved for special occasions or specific outfits.
Daily Wear:
- Compression Garments: Can be worn daily in cases of medical necessity or during recovery periods.
- Shapewear: Designed for daily use but should be worn for limited hours to avoid potential health risks.
8.3. Personal Comfort and Aesthetic Goals
Comfort:
- Compression Garments: Focus on functionality and support, may feel tighter due to medical-grade compression.
- Shapewear: Aim for a balance between comfort and aesthetics, often softer and more flexible.
Aesthetic Goals:
- Compression Garments: Not typically designed for aesthetics but for health benefits and performance.
- Shapewear: Specifically designed to enhance body appearance and fit seamlessly under clothes.
9. Garments vs. Shapewear:Making the Right Choice: Key Takeaways
Choosing between compression garments and shapewear depends on your specific needs, whether they are health-related, performance-based, or aesthetic. Here’s a quick summary to help you decide:
9.1. Choose Compression Garments If You Need:
- Improved Circulation: For medical conditions or post-surgery recovery.
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: For muscle support and quicker recovery.
- Long-Term Wear: For travel, prolonged standing or sitting, or chronic conditions.
9.2. Choose Shapewear If You Need:
- Body Contouring: For a smoother, more streamlined appearance under clothes.
- Confidence Boost: To feel more comfortable and confident in your outfits.
- Temporary Use: For special occasions, professional settings, or casual wear.
Share This Post:
Table of Contents
Most Popular

Custom backless shapewear for Spanish bridal boutiques and ateliers


Custom backless shapewear for French bridal gown designers and ateliers

Custom backless bridal shapewear development for Japan wedding labels
Get in touch with us
Related Posts

Custom backless shapewear for Spanish bridal boutiques and ateliers
Custom backless shapewear for Spanish bridal boutiques and ateliers is no longer an optional accessory—it is a decisive factor in whether an open-back wedding gown fits, photographs, and feels the

OEM backless wedding shapewear for German bridal gown manufacturers and retailers
OEM backless wedding shapewear has become a decisive category for German bridal gown manufacturers and retailers who design elegant open-back silhouettes while maintaining comfort, fit, and confidence for brides. The

Custom backless shapewear for French bridal gown designers and ateliers
For French bridal gown designers and ateliers, custom backless shapewear is no longer a niche accessory—it is a structural necessity. The conclusion is clear: without purpose-built, low-back or open-back shapewear,

Custom backless bridal shapewear development for Japan wedding labels
Custom backless bridal shapewear development for Japan wedding labels succeeds when brands start with a clear conclusion: the product must disappear visually while delivering stable shaping, comfort, and confidence through